第一章
Android是Google公司基于Linux平台开发的手机及平板电脑的操作系统。
一。安卓体系的具体结构
分层结构,由高到低分别是应用程序层、应用程序框架层、核心类层、Linux内核
1.应用程序层(Applications) 一个核心应用程序的集合,所有安装在手机上的应用程序都属于这一层,例如系统自带的联系人程序、短信程序等
2.应用程序框架层(Application Framework) 主要提供了构建应用程序时用到的各种API
3.核心类层(Libraries) 包含了系统库及Android运行时库。系统层这一层主要通过CC++库来位Android系统提供主要的特性支持。
4.Linux内核 为Android设备的各种硬件提供了底层的驱动
二。Dalvik虚拟机 1.定义 Google自己设计用于Android平台的虚拟机,可以简单地完成进程隔离和线程管理,并可以提高内存的使用效率。每个Android应用程序在底层都会对应一个独立的Dalvik虚拟机实例。
2.与Java虚拟机的不同 Java虚拟机: 基于栈的架构
栈是连续的内存空间,取出存入的速度比较慢
编译后文件:.java -> .class -> .jar
Dalvik虚拟机: 基于寄存器的架构
寄存器是CPU上的一块缓存,存取速度比从内存中快很多
编译后文件: .java -> .class -> .dex -> .odex
三。Android程序结构 1.manifests 思考题:清单文件的作用功能
存放AndroidManifest.xml 文件(清单文件),是整个项目的配置文件。四大组件都需要在这个文件中注册。
还可以在该文件中给程序添加权限。
清单文件中的配置的信息会添加到安卓系统中,程序运行时,系统会找到清单文件中的配置信息
四大组件注册 1.activity注册方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <activity android:label ="@string/app_name" android:launchMode ="singleInstance" android:name =".Day21_03_SmsActivity" > <intent-filter > <action android:name ="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name ="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter > </activity >
2.BroadcastReceiver静态注册方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <receiver android:name =".SmsReceiver" > <intent-filter > <action android:name ="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" /> </intent-filter > </receiver >
3.ContentProvider注册方法
1 2 3 4 5 <provider android:authorities ="com.aile.provider.student" android:name =".StudentProvider" > </provider >
4.Service服务(IntentService和service注册方法) 1 2 <service android:name =".MyService" > </service >
2.java 存放所有Java代码,可以创建多个包,每个包里可以存放不同文件或者Activity
3.res 存放资源。
drawable目录用于存放图片以及xml文件
layout存放布局文件
mipmap存放应用程序图标
4.Gradle Scripts 存放项目创建的相关文件,无需修改
第二章 一。布局 1.线性布局LinearLayout 1)orientation属性:
控制控件的排列方向
有vertical和horizontal(默认)
vertical为线性垂直显示
horizontal为线性布局水平显示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <LinearLayout xmlns:android ="" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:orientation ="vertical" > <Button > </LinearLayout >
2)wrap_content和match_parent
wrap_content:包括内容让当前控件根据内容大小自动伸缩
match_parent:填充父窗体由父容器大小决定控件大小
3)layout_weight权重
按钮1的权重值为1
计算方法: 1/(1+1+2) = 1/4
所以按钮1占一行的1/4
设置android:layout_width=”match_parent”后Button中的layout_width会失去作用,所以设置为0dp作为规范写法,不会影响效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="" "match_parent" "wrap_content" id ="@+id/btn_one android:layout_width=" 0 dp"wrap_content" "1" text ="按钮1" >id ="@+id/btn_two android:layout_width=" 0 dp"wrap_content" "1" text ="按钮2" >id ="@+id/btn_three" "0dp android:layout_height=" wrap_content" android:layout_weight=" 2 " android:text=" 按钮3 "> </LinearLayout>
2.相对布局RelativeLayout 默认采用的是相对布局
px: 像素
pt: 磅数
dp: 基于屏幕密度的抽象单位,不同设备希纳是效果不同
sp: 可伸缩像素
3.帧布局FrameLayout
布局属性
功能
属性值
android:foreground
设置前景图片(始终在所有子控件之上)
图片路径
android:foregroundGravity
前景图片显示位置
left right center
4.表格布局TableLayout
布局属性
功能
android:stretchColumns
设置该列被拉伸
android:shrinkColumns
设置该列被收缩
android:collapseColumns
设置该列被隐藏
控件属性
功能
android:layout_column
设置该单元显示位置
android:layout_span
设置该单元占据几列,默认为1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <TableLayout xmln:android ="" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:stetchColumns ="2" > //拉伸第三列<TableRow > <Button android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:layout_column ="0" android:text ="按钮1" /> <Button android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:layout_column ="1" android:text ="按钮2" /> </TableRow > </TableLayout >
5.绝对布局AbsoluteLayout 二。常用控件 1.TextView
控件属性
功能
android:text
android:textColor
android:textSize
android:textStyle
android:height
android:width
android:maxLength
android:password
android:gravity
设置文本位置
layout_width、layout_height和width 、height区别 1.
对于带layout前缀属性通常是相对父控件而言
不带是相对与控件本身而言
2.layout的可以单独使用,不带的不能单独使用
3.不带的只能设置为固定值
4.要使用不带的,就必须同时设置layout_width和layout_height属性
2.EditText
控件属性
功能
android:hint
没有输入内容时显示的提示文本
android:lines
固定行数决定EditText高度
android:editable
是否可编辑
android:scrollHorizontally
是否出现横拉条
可以设置android:maxLines来设置最大行数,超过行数会显示滚动条
1.布局中指定onClick属性 1 2 3 4 5 6 <Button android:id = "@id/btn_one" android:text = "按钮1" android:layout_width = "match_parent" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:onClick = "click" />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private Button myBtn_one;@Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);public void click (View v) {"按钮1点击" )
2.使用匿名内部类 1 2 3 4 5 <Button android:id = "@id/btn_two" android::text = "按钮2" android:layout_width = "match_parent" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private Button myBtn_two;@Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);new View .OnClickListener() {@Override public void onClick (View v) {"按钮2点击" );
3.在当前Activity中实现OnClickListener接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View .OnClickListener {private Button myBtn_two;private Button myBtn_one;@Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);this );this );@Override public void onClick (View v) {switch (v.getId() ){case R.id.btn_one:"按钮1" );break ;case R.id.btn_two:"按钮2" );break ;
RadioGrop是单选组合框,可容纳多个RadioButton
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:orientation ="vertical" > <RadioGroup android:id ="@+id/rdg" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:orientation ="vertical" > <RadioButton android:id ="@+id/r_btn" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:textSize ="25dp" android:text ="女" > </RadioButton > <RadioButton android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:textSize ="25dp" android:text ="男" android:checked ="true" > </RadioButton > </RadioGroup > </LinearLayout >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View .OnClickListener {private RadioGroup radioGroup@Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);new RadioGroup .OnCheckChangeListener() {@Override public void OnCheckChange (RadioGroup group) {if (checkedId == R.id.r_btn) {else {
5.消息对话框 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);R .layout.activity_main);Toast .makeText(this , "Hello,Toast" , Toast .LENGTH_SHORT ).show();
三。LogCat的使用 Android中的命令行工具,用于获取程序成启动到关闭的日志信息。
等级 等级由低到高排
import android.util.Log
1.Verbose 全部消息 (黑色)
2.Debug 调试信息(蓝色)
3.Info 一般信息(绿色)
4.Warning 警告信息(橙色)
5.Error 错误信息(红色)
6.Assert
过滤器 1.Filter Name 过滤器的名称
2.by Log Tag 根据定义的Tag过滤,通常使用类名
3.by Log Message 根据输出内容过滤信息
4.by PID 根据进程id
5.by Application Name 根据应用名称过滤信息
6.by Log Level 根据日志的级别过滤信息
四。单元测试 单元测试是指应用程序开发过程中对最小的功能模块进行测试,可以在完成某个功能之后对该功能进行单独测试,而不需要把应用程序安装到手机或启动模拟器再对各项功能进行测试,可以提高开发效率和质量
Android Studio在创建项目时就默认创建了一个androidTest包和ApplicationTest类,把测试的功能模块写入此类即可
进行单元测试时的步骤 1.在ApplicationTest类中添加一个test()测试方法
2.单独选择test方法进行运行查看结果
第三章 一。Activity创建
包名处右键—>new—->Activity—->Empty Activity
输入Activity Name和Layout Name、Package name
创建的activity.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class ShopActivity extends AppCompatActivity {@Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);
手动注册
1 2 3 在AndroidManifest.xml中添加<activity android:name =".ActivityExample" > </activity >
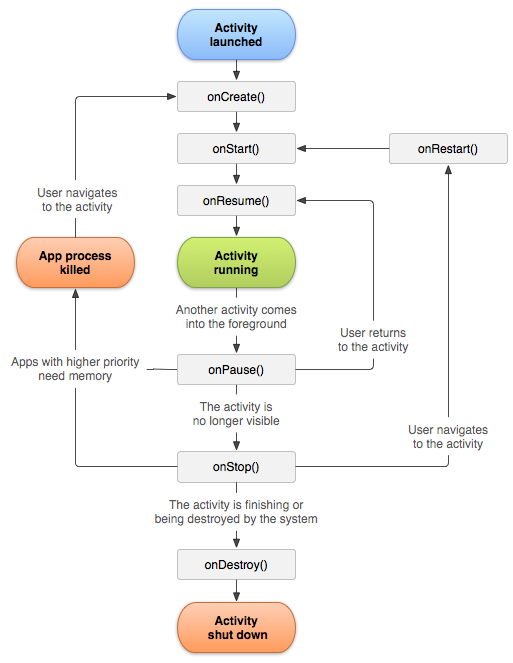
二。生命周期
1.生命周期状态
onCreate() —> onStart() —> onResume() —> onPause() —> onStop() —> onDestroy()
1)启动状态
2)运行状态
3)暂停状态
4)停止状态
5)销毁状态
2.生命周期方法 1.onCreate()方法
创建时调用
1 2 3 4 5 @Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(saveInstanceState);
2.onStart()方法
在Activity即将可见时调用
1 2 3 4 @Override protected void onStart () {super .onStart();
3.onResume()方法
在Activity获取焦点 开始与用户交互时调用
1 2 3 4 @Override protected void onResume () {super .onResume();
4.onPause()方法
当前Activity被其他Activity覆盖或锁屏时调用
当执行到onPause()方法失去焦点 , 重新回到前台会执行onResume()方法
1 2 3 4 @Override protected void onPause () {super .onPause();
5.onStop()方法
Activity对用户不可见时
1 2 3 4 @Override protected void onStop () {super .onStop();
6.onDestroy()方法
Activity销毁
1 2 3 4 @Override protected void onDestroy () {super .onDestroy();
7.onRestart()方法
Activity从停止状态再次启动
1 2 3 4 @Override protected void onRestart (super .onRestart ();
三。Activity之间的跳转 Intent称为意图,是程序中各组件进行交互的一种重要方式,不仅可以将指定当前组件要执行的动作,还可以在不同组件之间进行数据传递。一般用于启动Activity、Service以及发送广播等
1.打开浏览器 1 2 3 4 5 6 @Override public void onClick (View v) {Intent intent = new Intent ();"android.intent.action.VIEW" );"http://www.baidu.com" ));
2.数据传递
将要传递的数据暂存到Intent中,启动另外一个Activity后从Intent中取出数据即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Intent intent = new Intent (this ,Activity.class);"extra_data" ,"hello" ); Intent intent = getIntent();String data = intent.getStringExtra("extra_data" );
3.数据回传
startActivityForResult(Intent intent,int requestCode)
setResult(int resultCode,Intent data)方法
不过现在已经弃用
代替为registerForActivityResult()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Activity01中Intent intent = new Intent (this ,Activity02.class);1 ) Intent intent = new Intent ();"extra_data" ,"hello" ); 1 ,intent); @Override protected void onActivityResult (int requestCode,int resultCode,Intent data) {super .onActivityResult(requestCode,resultCode,data);if (requestCode == 1 ) {if (resultCode == 1 ) {String string = data.getStringExtra("extra_data" );
第四章 一。五种存储方式 1.文件存储 读取/写入文件,通过openFileInput()和openFileOutput()方法读取设备上的文件。与Java中实现I/O程序一致
存储位置
默认存储在 data/data//files/ 目录下
1 2 FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(String name,int mode); FileInputStream fis = openFileInput(String name);
“name” 表示文件名
“mode” 表示文件的操作模式
MODE_PRIVATE: 文件只能被当前程序读写
MODE_APPEND: 文件内容可以追加
MODE_WORLD_READABLE: 文件的内容可以被其他程序读
MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE: 文件的内容可以被其他程序写
数据存储到文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 String name = "data.txt" ;String data = "hello" ;try {catch (Exception e) {
数据读取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 String content = "" ;try {"data.txt" );byte [] buffer = new byte [fis.available()]; new String (buffer) catch (Exception e) {
2.SharedPreferences 用XML格式将数据存储到设备中,可以存储应用程序的各种配置信息(用户名、密码等)
存储位置
data/data//shared_prefs文件夹中
存储方式
通过key/value(键值对)的形式将数据保存在XML文件中
value值的类型只能是Float,Int,Long,Boolean,String,StringSet类型数据
1.存储数据
1.调用getSharedPreferences(String name,int mode)方法获取实例对象
2.调用SharedPreferences的edit方法获取到可编辑的Editor对象
3.通过putString(),putInt()方法存储数据
4.通过commit()方法提交数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 SharedPreferences sp = getSharedPreferences("data" ,MODE_PRIVATE);Editor editor = sp.edit();"name" ,"hello" );"age" ,9 );"name" );
2.获取数据
1.获取SharedPreferences对象
2.通过getxxx()方法获取到对应的key值
1 2 SharedPreferences sp = getSharedPreferences("data" ,MODE_PRIVATE);String data = getSring("name" ,"" )
3.SQLite数据库 Android自带的一个轻量级数据库,支持基本SQL语法,一般使用它作为复杂数据的存储引擎。
详细见第五章
4.ContentProvider 四大组件之一,主要用于应用程序之间的数据交换 ,可以将自己的数据共享给其他应用程序使用
5.网络存储 将数据存储在服务器上
二。XML解析 1.DOM解析 2.SAX解析 3.PULL解析 三。JSON解析 第五章 考编程题查询数据并展示在listview中
看p138的绿豆通讯录
一。数据库的创建
1.创建一个类继承SQLiteOpenHelper
2.重写onCreate()和onUpgrade()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class MyHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {public MyHelper (Context context) {super (context, "ahao" ,null ,2 );public void onCreate (SQLiteDatabase db) {"CREATE TABLE information(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,name VARCHAR(20), price Integer)" );public void onUpgrade (SQLiteDatabase db,int oldVersion,int newVersion) {
二。增删改查 1.增加数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public void insert (String name,String price) {SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase(); ContentValues values = new ContentValues (); "name" ,name); "price" ,price);long id = db.insert("information" ,null ,values);
2.修改数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public int update (String name, String price) {SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();ContentValues values = new ContentValues ();"price" ,price);int number = db.update("information" ,values,"name=?" ,new String []{name});return number;
3.删除数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 public int delete (long id) {SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();int number = db.delete("information" ,"_id=?" ,new String []{id+"" });return number;
4.查询数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public boolean find (long id) {SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();Cursor cursor = db.query("information" ,null ,"_id=?" ,new String []{id+"" },null ,null ,null );boolean result = cursor.moveToNext();return result;
使用execSQL()方法操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "insert into information (name,price) values (?,?)" ,new Object []{name,price});"update information set name=? where price =?" ,new Object []{name,price});"delete from information where _id = 1" );Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from person where name=?" ,new String []{name});
三。SQLite中的事务
事务时一个对数据库执行工作的单元,是针对数据库的一组操作,可以由一条或多条SQL语句构成。
事务是以逻辑顺序完成的工作单位或序列,可以由用户手动操作完成,也可以由某种数据库程序自动完成
同一事务的操作具备同步的特点,一条语句无法执行,所有语句都不会执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 db.beginTransaction(); try {catch (Exception e) {"处理失败" ,e.toString());finally {
当执行到endTransaction()方法时,首先会检查是否有事务执行完成标记,有则提交数据,无则回滚数据
四。ListView控件
ListView是一个列表视图,由很多Item(条目)组成,每个Item的布局时相同的,Item布局单独使用一个XML定义
1.数据适配器 1)BaseAdapter 基本的适配器,实际上是一个抽象类,通常在使用自定义适配器时需要继承BaseAdapter。有四个抽象方法
方法
功能描述
public int getCount()
得到Item条目的总数
public Object getItem(int position)
根据position(位置)得到某个Item的对象
public long getItemId(int postion)
根据position得到某个Item的id
public View getView(int position, View converView, ViewGroup parent)
得到相应position对应的Item视图,position是当前Item的位置,converView用于复用旧视图,parent用于加载XML布局
2)SimpleAdapter 继承自BaseAdapter,实现对四个抽象方法进行了封装。使用SimpleAdapter进行数据适配时,只需要在构造方法中传入相应的参数即可
1 public SimpleAdapter(Context context , List<? extends Map<String,?>> data , int resource , String[] from ,int [] to ) ;
Context context: Context上下文对象
List> data: 数据集合,data中每一项对应ListView中每一项数据
int resource: Item布局的资源id
String[] from: Map集合里面的key值
int[] to: Item布局相应的控件id
3)ArrayAdapter BaseAdapter的子类,只需要在构造方法中传入相应参数即可。通常用于设配TextView控件。
示例 activity_main.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools ="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" tools:context =".ShopFragment" > <ListView android:id ="@+id/list_view" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:layout_below ="@id/shop_image" android:divider ="#d0d0d0" android:dividerHeight ="1dp" /> </RelativeLayout >
item.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width ="match_parent" android:layout_height ="match_parent" android:gravity ="center_vertical" > <ImageView android:layout_width ="48dp" android:layout_height ="48dp" android:id ="@+id/image" android:background ="@drawable/shop" > </ImageView > <TextView android:id ="@+id/item_tv" android:layout_width ="wrap_content" android:layout_height ="wrap_content" android:text ="我的item布局" android:textSize ="18sp" > </TextView > </LinearLayout >
MainActivity.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class ShopActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private ListView listView;private String[] name = {"京东" , "pdd" };private int [] icons = {R.drawable.apple,};@Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);ListView listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list_view);MyBaseAdapter myBaseAdapter = new MyBaseAdapter ();class MyBaseAdapter extends BaseAdapter {@Override public int getCount () {return name.length;@Override public Object getItem (int position) {return name[position];@Override public long getItemId (int position) {return position;@Override public View getView (int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {View view = View.inflate(MainActivity.this , R.layout.item, null ); TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.item_tv);ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.shop_image);return view;
第六章
当产生一个广播事件时,可以有多个BroadcastReceiver 接收并处理数据。
广播接收者只需要在清单文件或代码中进行注册并指定要接收的广播事件,创建一个类继承自BroadcastReceiver类,重写onReceive()方法,在方法中处理广播事件即可
一。基础 1.创建 new —-> other —-> Broadcast Receiver
注册 1)静态注册 AndroidMainfest.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <application > <receiver android:name =".MyReceiver" android:enable ="true" android:exported ="true" > </receiver > </application >
MyReceiver.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceivver {public MyReceier () {@Override public void onReceive (Context context, Intent intent) {
2)动态注册 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);MyReceiver receiver = new MyReceiver ();String action = "android.provider.Telephony.SMS_RECEIVED" ;IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter (action);@Override protected void onDestroy () {super .onDestroy();
2.拦截电话案例 广播接收者OutCallReceiver 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class OutCallReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {@Override public void onReceive (Context context, Intent intent) {String number = getResultData();SharedPreferences sp = context.getSharedPreferences("config" ,Context.MODE_PRIVATE);String number2 = sp.getString("name" ,"" );if (number.equals(number2)){null );else {
AndroidManifest.xml中添加权限
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <application > <receiver android:name =".OutCallReceiver" > <intent-filter > <action android:name ="android.intent.action.NEW_OUTGOING_CALL" /> //权限</intent-filter > </receiver > </application >
二.广播类型 1.有序广播
可以被拦截
按照接收者声明的优先级别依次接收,发送广播时,只有一个广播接收者能够接收此消息,当此广播接收者中逻辑执行完毕后,广播才会继续传递。
优先级设置
在注册广播接收者时,在标签中使用priority属性设置优先级
1 <intent-filter android:priority ="100" >
属性值越大,优先级越高
优先级相同时,先注册的优先级高
2.无序广播 完全异步执行,发送广播时,所有监听这个广播的广播接收者都会接收到此广播消息,但接收和执行的顺序不确定
拦截广播案例 发送有序广播
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public void send (View view) {Intent intent = new Intent ();"Intercept_Stitch" );null );
添加广播接收者
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class MyBroadcastReceiverOne extends BroadcastReceiver {@Override public void onReceive (Context context, Intent intent) {"广播接收者1接收到广播事件" )
注册广播接收者
1 2 3 4 5 <receiver android:name =".MyBroadReceiverTwo" > <intent-filter android:priority ="1000" > <action android:name ="Intercept_Stitch" > </action > </intent-filter > </receiver >
拦截有序广播
优先级高的广播接收者可以拦截收到的广播
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class MyBroadcastReceiverOne extends BroadcastReceiver {@Override public void onReceive (Context context, Intent intent) {"广播接收者1接收到广播事件" )
指定广播接收者
1 2 3 4 5 6 Intent intent = new Intent ();"Intercept_Stitch" );MyBroadcastReceiverThree receiver = new MyBroadcastReceiverThree null ,receiver,null ,0 ,null ,null );
第七章
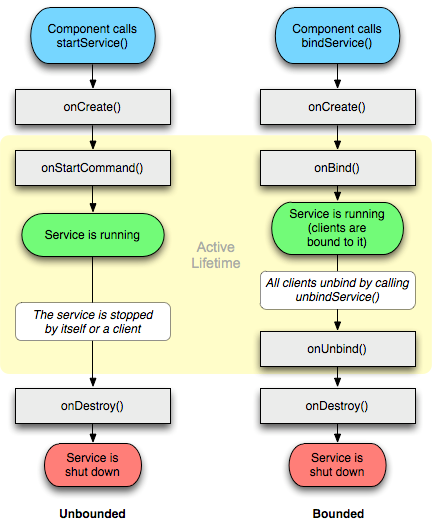
Service(服务)是一个长期运行在后台的用户组件,没有用户界面。因此服务更适合执行一段事件而又不需要显示界面的后台操作(下载数据、播放音乐等)
一。创建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class MyService extends Service {public MyService () {@Override public IBinder onBind (Intent intent) {throw new
默认包含一个构造方法和一个onBind()方法
onBind()用于绑定服务,放回一个IBinder对象
注册
name中填的是服务的路径
enabled:是否实例化该组件
exported:该服务是否能够被其他应用程序调用或交互
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <application > <service android:name =".MyService" android:enabled ="true" android:exported ="true" > </service > </application >
二。生命周期 服务的启动方式有两种,分别是**startService()方法和 bindService()**方法
方法
onCreate() :第一次创建服务时执行onDestory() :服务被销毁时执行onStartCommand() : 通过startService()方式启动服务onBind() : 通过bindService()方法启动服务onUnbind() : 客户端调用unBindService()断开服务器绑定时执行
启动 1.startService 方式 三。服务的通信
通过绑定方式 开启服务后,服务与Activity可以通信。
必须保证服务是以绑定方式开启的,否转无法进行通信和数据交换。
1.本地服务通信
应用程序内部的通信
2.远程服务通信
两个应用程序之间的通信
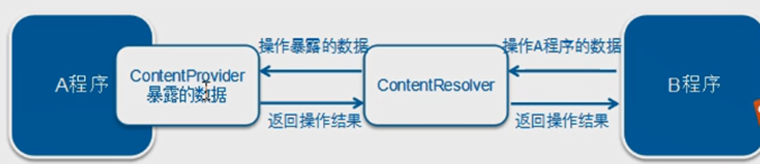
注意看p175 第八章 一。简介 ContentProvicer内容提供者是四大组件之一,功能是在不同程序之间实现数据共享 。
文件存储、SharePreferences存储、数据库存储这些只能在当前应用程序中访问
要访问ContentProvider中共享的数据,一定要借助ContentProvider类
Uri
为内容提供者的数据建立了唯一的标识符。主要由scheme、authoritied和path 三部分组成
scheme:
“content://“ 是一个标准前缀,表明这个数据被ContentProvider所控制
authority:
在创建内容提供者时指定的authorities属性值,用于区分不同的应用程序
一般采用程序包名命名
path:
二。内容提供者的创建 增删改查
insert()
delete()
update()
query()
注册 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <application > <provider android:authorities ="cn.app" android:name =".MyContentProvider" android:enabled ="true" android:exported ="true" > </provider > </application >
三。使用 1.访问内容提供者 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://cn.app/person" );ContentResolver resolver = context.getContentResolver();Cursor cursor = resolver.query(uri, new String [] { "address" , "date" , "type" , "body" },null ,null ,null )while (cursor.moveToNext()) {String address = cursor.getString(0 );long date = cursor.getLong(1 );int type = cursor.getInt(2 );String body = cursor.getString(3 );
案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://sms/" );ContentResolver resolver = context.getContentResolver();Cursor cursor = resolver.query(uri, new String [] { "address" , "date" , "type" , "body" },null ,null ,null )if (cursor != null && cursor.getCount() > 0 ) {while (cursor.moveToNext()) {String address = cursor.getString(0 );long date = cursor.getLong(1 );int type = cursor.getInt(2 );String body = cursor.getString(3 );
四。内容观察者
观察指定Uri所代表的数据,数据变化时会触发ContentObserver的onChange()方法。
在onChange()方法中使用ContentResovler可以查询到变化的数据
第九章 GET方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 String path = "http://192.168.1.1:8080/web?username=" +URLEncoder.encode("zhangsan" )+"&password=" +URLEncoder.encode("123" );URL url = new URL (path)HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();"GET" );5000 );int responsecode = conn.getResponseCode;if ( responsecode == 200 ) {InputStream is = conn.getInputStream
POST方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 String path = "http://192.168.1.1:8080/web" ;URL url = new URL ();HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) conn.openConnection();"POST" );5000 );String data = "username=" +URLEncoder.encode("zhangsan" )+"&password=" +URLEncoder.encoder("123" )"Content-Type" , "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" )"Content-Length" , data.length() + "" );true ); OutputStream os = conn.getOutputStream(); int code = conn.getRequestCode();if ( code == 200 ) {InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
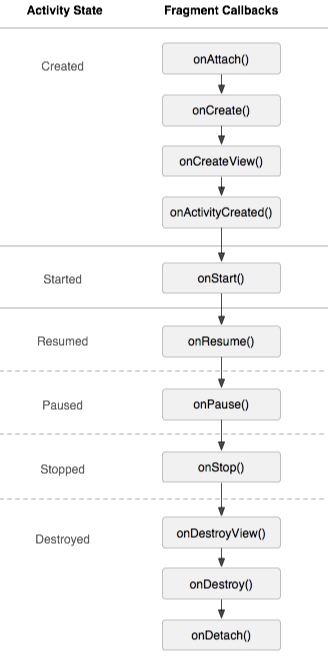
第十章 Fragment
Fragment不能独立存在,必须嵌入到Activity中使用
Activity暂停时,它所拥有的Fragment都暂停
Activity销毁时,它所拥有的Activity都销毁
生命周期方法
onAttach() : 当Fragment和Activity建立关联时调用
onCreateView(): 创建视图
onDetach(): 当Fragment和Activity解除关联时调用
注册
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <fragment android:id ="@id/fragment" android:name ="" android:layout_width ="" android:layout_height ="" > </fragment >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private List<Fragment> fragmentList;@Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);new ArrayList <>(Fragment) ();new Fragment1 ());new Fragment2 ());new Fragment3 ());FragAdapter adapter = new FragAdapter (getSupportFragmentManager(), fragments);ViewPager vp = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.viewpager);